ToolBoxに PySide のWidgetを追加してみよう
この記事はMaya Advent Calendar 2021の1日目の記事です 今年もAdventCalendarの季節がやってまいりました!! amanatsu-knitさんにはいつも感謝ですね!
MayaのUIを拡張したいなーなんて思ったことありませんか?ここにボタンがあれば。。。ここにメニュー追加したいなんて。。。そういった拡張をする場合はOpenMayaUIを使用して、MayaのUI情報をQtに変換しないといけないのですが今回は一例を紹介したいと思います
ToolBoxにボタンを追加

ToolBoxは通常Mayaの横にあるSelectToolやMoveToolのボタンのあるウィジェットのことでここにQPushButtonを埋め込んでみたいと思います 埋め込むコードを書く前にはこのToolBoxのUI情報を取得するための準備をしていきましょう OpenMayaUI.MQtUtilとshibokenを使用してMayaUIをQtにラップインスタンスしたオブジェクトを取得できるクラスを作っていきます
OpenMayaUI.MQtUtilはMayaのUI を支える Qt コントロールにアクセスするための基本的なメソッドがいくつか用意されており、独自のPySideWindowとMayaMainWindowに親子付けをする際やMaya上のUI情報を取得したい際などに使用します
shibokenとはMaya™のようなPythonスクリプトを提供するQtベースのプログラムとPySideを統合したり、デバッグの際に必要になるPythonモジュールです
まずはMayaの情報を取得するクラスを用意してみましょう
import maya.OpenMayaUI as OpenMayaUI
import shiboken2 as shiboken
from PySide2.QtWidgets import *
from PySide2.QtCore import *上のコードのようにimportモジュールを事前に用意しておきます
今回作るクラスは普段でも使用できるようなライブラリのようなクラスを作っていきましょう
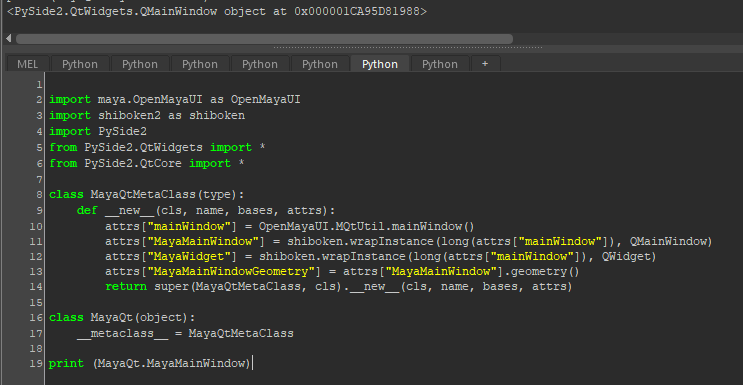
MayaQtMetaClassというクラスの__new__でOpenMayaUI.MQtUtil.mainWindow()とそれを元にラップインスタンスしたMayaMainWindow、MayaWidget、MayaMainWindowGeometryのインスタンスを生成します
class MayaQtMetaClass(type):
def __new__(cls, name, bases, attrs):
attrs[mainWindow] = OpenMayaUI.MQtUtil.mainWindow()
attrs[MayaMainWindow] = shiboken.wrapInstance(long(attrs[mainWindow]), QMainWindow)
attrs[MayaWidget] = shiboken.wrapInstance(long(attrs[mainWindow]), QWidget)
attrs[MayaMainWindowGeometry] = attrs[MayaMainWindow].geometry()
return super(MayaQtMetaClass, cls).__new__(cls, name, bases, attrs)次にMayaQtというクラスを用意します
このクラスはmayaのUIオブジェクト名と指定したウィジェットに変換するmayaToPySideとQtからMayaのfullNameを取得できるqtToMayaFullNameいうクラスメソッドを持っており、__metaclass__に先ほど作成したMayaQtMetaClassが設定されているクラスです
class MayaQt(object):
__metaclass__ = MayaQtMetaClass
@classmethod
def mayaToPySide(cls, name, toType):
ptr = OpenMayaUI.MQtUtil.findControl(name)
if not ptr:
ptr = OpenMayaUI.MQtUtil.findLayout(name)
if not ptr:
ptr = OpenMayaUI.MQtUtil.findMenuItem(name)
if not ptr:
return None
return shiboken.wrapInstance(long(ptr), toType)
@classmethod
def qtToMayaFullName(cls, widget):
return OpenMayaUI.MQtUtil.fullName(shiboken.getCppPointer(widget)[0])
class MayaQt(object):
__metaclass__ = MayaQtMetaClassMayaQtの__metaclass__にMayaQtMetaClassを設定することにより、変数を取得することができます
@classmethod
def mayaToPySide(cls, name, toType):
ptr = OpenMayaUI.MQtUtil.findControl(name)
if not ptr:
ptr = OpenMayaUI.MQtUtil.findLayout(name)
if not ptr:
ptr = OpenMayaUI.MQtUtil.findMenuItem(name)
if not ptr:
return None
return shiboken.wrapInstance(long(ptr), toType)mayaToPySideではMayaUIのオブジェクトを指定し、ポインターを取得します
そして、取得したポインターから指定したクラスのインスタンスとして取得することができます
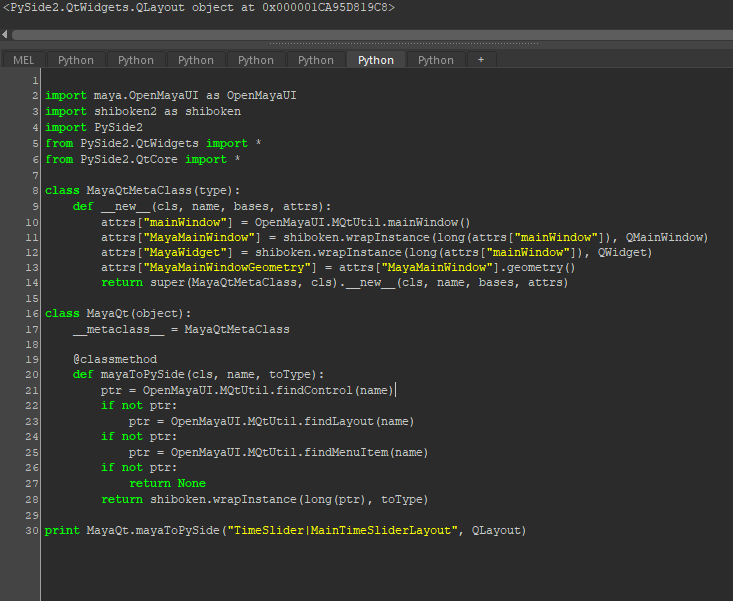 例えば、MayaのTimeSliderのレイアウトをQLayoutとして取得したい場合はnameに
例えば、MayaのTimeSliderのレイアウトをQLayoutとして取得したい場合はnameにTimeSlider|MainTimeSliderLayoutとtoTypeにQLauoutを指定すれば取得できます
@classmethod
def qtToMayaFullName(cls, widget):
return OpenMayaUI.MQtUtil.fullName(shiboken.getCppPointer(widget)[0])mayaToPySideではMayaUIのインスタンスを指定することでインスタンスのメモリアドレスを取得し、UI 要素の完全な階層をもった名前を取得することができます
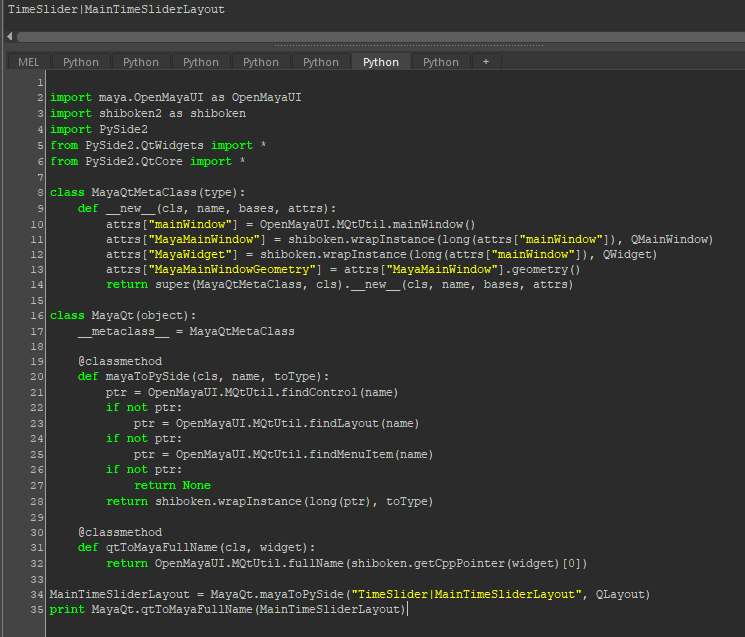 先ほどmayaToPySideで取得したインスタンスを指定すると
先ほどmayaToPySideで取得したインスタンスを指定するとTimeSlider|MainTimeSliderLayoutが取得できます
では実際に作成したクラスを使用してToolBoxのWindow情報を取得し、QPushButtonを設定してみます まずはToolBoxをQDockWidgetに変換します
ToolBoxWidget = MayaQt.mayaToPySide(name=ToolBox, toType=QDockWidget)そしてこの変換したToolBoxWidgetのchildrenをloopなどを使って調べていきます
for child in ToolBoxWidget.children():
if type(child) == QWidget:
MainToolboxLayout = child
if type(child) == QVBoxLayout:
ToolBox = childdef getWidgetChildren(widget):
childrenDict = {}
def getWidgetChildrenClosure(widget, dict):
for child in widget.children():
childrenDict[child.objectName()] = child
getWidgetChildrenClosure(child, childrenDict[child.objectName()])
for child in widget.children():
childrenDict[child.objectName()] = child
getWidgetChildrenClosure(child, childrenDict[child.objectName()])
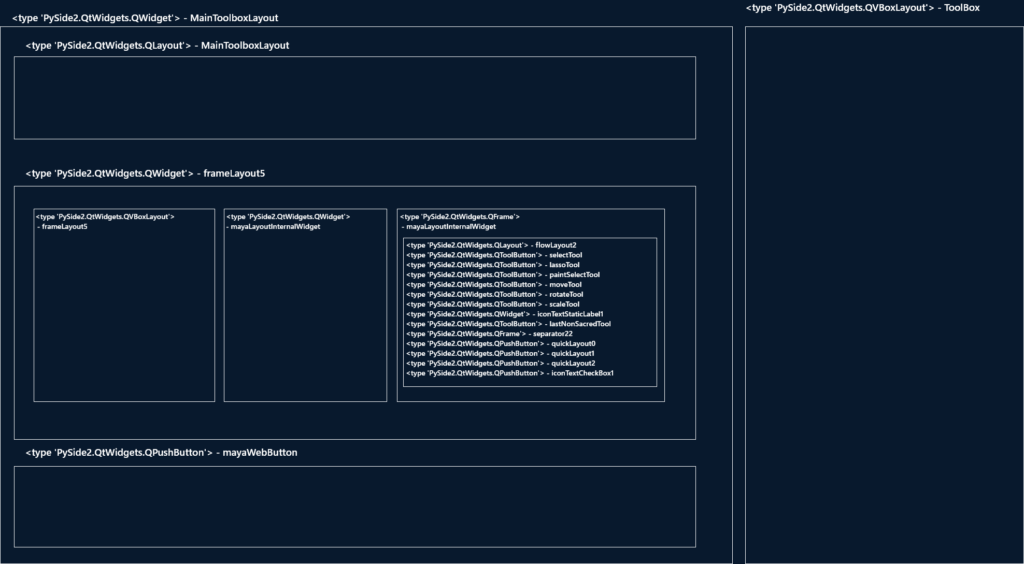
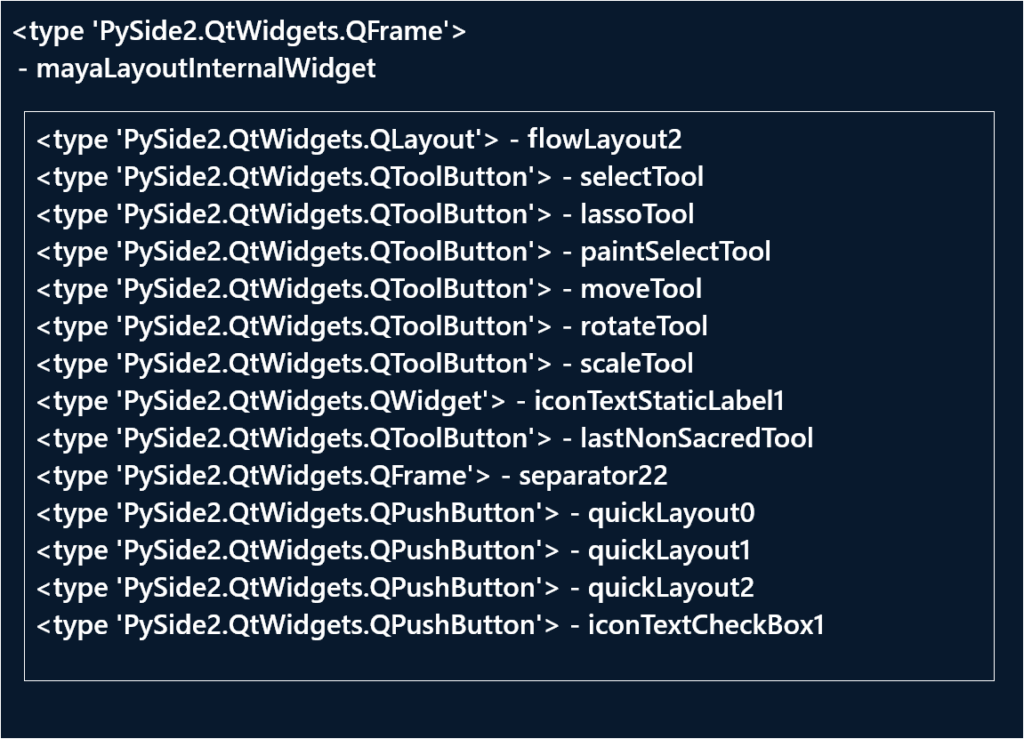
return childrenDictどうやらQFrameタイプのmayaLayoutInternalWidgetというオブジェクトのflowLayout2(Maya起動時やUI表示時の設定などによってオブジェクト名が異なる場合があります)にボタンがレイアウトされているようです。ということはここにaddWidgetすればボタンを追加できるということがわかります MayaのUIの構成を知りたい場合は下のコードのようにループしながら一つ一つ調べていくといいです
import maya.OpenMayaUI as OpenMayaUI
import shiboken2 as shiboken
import PySide2
from PySide2.QtWidgets import *
from PySide2.QtCore import *
class MayaQtMetaClass(type):
def __new__(cls, name, bases, attrs):
attrs[mainWindow] = OpenMayaUI.MQtUtil.mainWindow()
attrs[MayaMainWindow] = shiboken.wrapInstance(long(attrs[mainWindow]), QMainWindow)
attrs[MayaWidget] = shiboken.wrapInstance(long(attrs[mainWindow]), QWidget)
attrs[MayaMainWindowGeometry] = attrs[MayaMainWindow].geometry()
return super(MayaQtMetaClass, cls).__new__(cls, name, bases, attrs)
class MayaQt(object):
__metaclass__ = MayaQtMetaClass
@classmethod
def mayaToPySide(self, name, toType):
ptr = OpenMayaUI.MQtUtil.findControl(name)
if not ptr:
ptr = OpenMayaUI.MQtUtil.findLayout(name)
if not ptr:
ptr = OpenMayaUI.MQtUtil.findMenuItem(name)
if not ptr:
return None
return shiboken.wrapInstance(long(ptr), toType)
MayaQt.mainWindow
ToolBoxWidget = MayaQt.mayaToPySide(name=ToolBox, toType=QDockWidget)
for child in ToolBoxWidget.children():
if type(child) == QWidget:
MainToolboxLayout = child
if type(child) == QVBoxLayout:
ToolBox = child
for child in MainToolboxLayout.children():
if type(child) == QWidget:
frameLayout5 = child
if type(child) == QPushButton:
mayaWebButton = child
if type(child) == QLayout:
MainToolboxLayout = child
for child in frameLayout5.children():
if type(child) == QVBoxLayout:
frameLayout5 = child
if type(child) == QWidget:
mayaLayoutInternalWidgetQWidget = child
if type(child) == QFrame:
mayaLayoutInternalWidgetQFrame = child
for child in mayaLayoutInternalWidgetQWidget.children():
if type(child) == QVBoxLayout:
mayaLayoutInternalWidget = child
for child in mayaLayoutInternalWidgetQFrame.children():
if type(child) == QWidget:
flowLayout2 = child
for child in flowLayout2.children():
if type(child) == QLayout:
flowLayout2QLayout = child
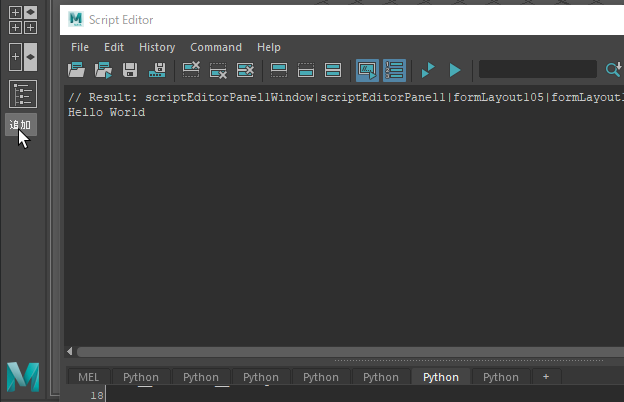
def printText():
print (Hello World)
btn = QPushButton(u追加)
btn.clicked.connect(printText)
flowLayout2QLayout.addWidget(btn)めぼしがついているなら下のコードのようにやってもいいかもしれません
import maya.OpenMayaUI as OpenMayaUI
import shiboken2 as shiboken
import PySide2
from PySide2.QtWidgets import *
from PySide2.QtCore import *
class MayaQtMetaClass(type):
def __new__(cls, name, bases, attrs):
attrs[mainWindow] = OpenMayaUI.MQtUtil.mainWindow()
attrs[MayaMainWindow] = shiboken.wrapInstance(long(attrs[mainWindow]), QMainWindow)
attrs[MayaWidget] = shiboken.wrapInstance(long(attrs[mainWindow]), QWidget)
attrs[MayaMainWindowGeometry] = attrs[MayaMainWindow].geometry()
return super(MayaQtMetaClass, cls).__new__(cls, name, bases, attrs)
class MayaQt(object):
__metaclass__ = MayaQtMetaClass
@classmethod
def mayaToPySide(cls, name, toType):
ptr = OpenMayaUI.MQtUtil.findControl(name)
if not ptr:
ptr = OpenMayaUI.MQtUtil.findLayout(name)
if not ptr:
ptr = OpenMayaUI.MQtUtil.findMenuItem(name)
if not ptr:
return None
return shiboken.wrapInstance(long(ptr), toType)
@classmethod
def qtToMayaFullName(cls, widget):
return OpenMayaUI.MQtUtil.fullName(shiboken.getCppPointer(widget)[0])
ToolBoxWidget = MayaQt.mayaToPySide(name=ToolBox, toType=QDockWidget)
def getWidgetChildren(widget):
childrenDict = {}
def getWidgetChildrenClosure(widget, dict):
for child in widget.children():
childrenDict[child.objectName()] = child
getWidgetChildrenClosure(child, childrenDict[child.objectName()])
for child in widget.children():
childrenDict[child.objectName()] = child
getWidgetChildrenClosure(child, childrenDict[child.objectName()])
return childrenDict
TBWChildrenDict = getWidgetChildren(ToolBoxWidget)
flowLayout2QLayout = TBWChildrenDict['flowLayout2']
def printText():
print (Hello World)
btn = QPushButton(u追加)
btn.clicked.connect(printText)
flowLayout2QLayout.addWidget(btn)MayaのUI自体を拡張するのも結構おもしろいので是非MayaのUIの拡張をしてみてください
Maya Python Advent Calendar 2021の2日目の記事は9bozさんのdraggerContext について何か書きますです




ディスカッション
コメント一覧
まだ、コメントがありません